In this Your EV Finder article, I will share the quick history of the lead-acid battery, the nickel-cadmium battery, the nickel-metal hydride battery, the lithium-ion battery and the solid-state battery. As we know, we are living in the age of technology which means EVs(electric vehicles) are now gaining more attention as compared to Petrol or Diesel. So let's start exploring the core and historical details of the mentioned batteries. In 1860, the Frenchman Gaston Planté invented the first rechargeable battery based on lead–acid chemistry. It was named the most successful secondary battery of all ages. In terms of recycling several companies working hard to make lightweight batteries, storage capacity, affordable production costs, lifespan, recharging capacity and environmental impact. For your information, Hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and all-electric vehicles use battery packs.
EV Future Battery: 500 miles on a single charge
In 2023-2024, there are several battery types available like lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, lead-acid, and ultracapacitors. In future, we will see technology such as solid-state batteries and I am sure that it will change the way people think about electric cars. Yes, of course, the upcoming technology will provide EV vehicle range of over 500 miles on a single charge.
History of the lead-acid battery
Invented in 1859, the lead-acid battery is available in several vehicles in 2023-2024. As per the historical data, back in 1899, the electric vehicle “La Jamais contente” (“The Never Happy”) featured this technology to exceed 100 km/h. Currently, lead-acid batteries become less choice, but to power the electrical circuit of accessories or components specific to combustion engines like the starter it is still alive.
History of the nickel-cadmium battery
If you were born in the 90s like me, then you might know the nickel-cadmium technology. But somehow it created an issue from the memory effect, a physical phenomenon that sees the battery’s performance decline if it is subject to partial “charge-drain” cycles. Now, the Ni-Cd batteries are prohibited due to the toxicity of cadmium.
History of the nickel-metal hydride battery
The nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH) battery was so popular as it avoid heavy metals. This portable rechargeable battery technology was the most economical at the beginning of the 2000s and it was the first choice for the hybrid vehicle market.
History of the lithium-ion battery
The lithium-ion battery was developed in the '90s and gained popularity in both transportation and in the consumer electronics industry. Renault uses lithium-ion technology for ZOE and the other electric vehicles in the range. Moreover, the Group is working on incorporating its batteries into a circular economy setup aiming to extend their lifespan as much as possible.
History of the solid-state battery
Toyota has confirmed that it has made a breakthrough that will allow “game-changing” solid-state batteries to go into production by 2028. By using the solid-state battery electric cars will get a range of 1200 kilometres with a charging time of just 10 minutes.
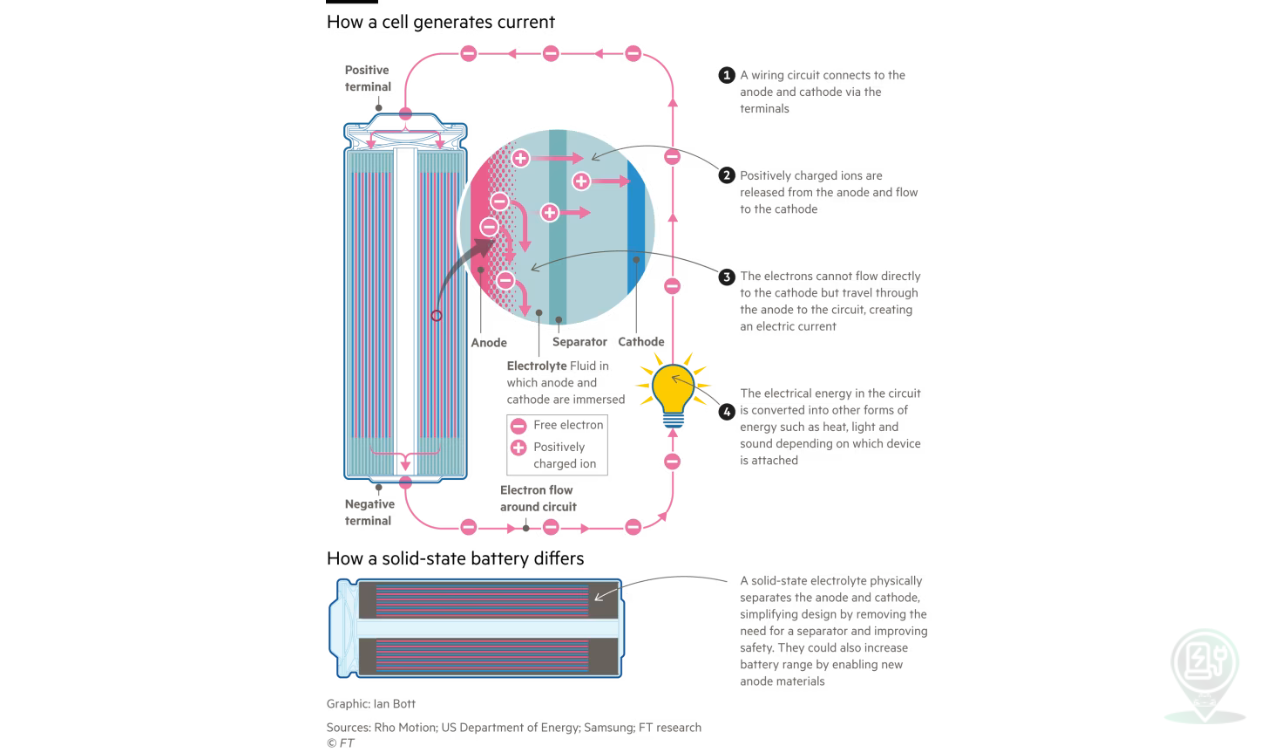
What are solid-state batteries?
The lithium-ion batteries which are currently available in our phones, laptops and electric cars have a liquid electrolyte, through which ions flow in one direction to charge the battery and the other direction when it is being drained. Solid-state batteries, as the name suggests, replace this liquid with a solid material. The principle behind it consists of replacing the battery’s liquid electrolyte with a solid material that can take the form of a plastic polymer, compacted inorganic powders or a mixture of the two. At the moment, China has the potential to dominate the next stage of the industry because of its leadership in both battery technology and manufacturing: it produced more than 75 per cent of batteries globally last year, according to the International Energy Agency.

.png)
.png)
